|
| Interesting Facts |
|---|
| * The size of Flying Fish depends on the species. On average, they are usually 7 to 12 inches long. |
| * The upper-side of the body of Flying Fish is bluish-grey. Their belly is grayish-silver. Flying Fish have a forked tail and the lower piece of the tail is longer than the upper piece. |
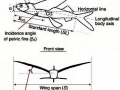
| * Pectoral fins of Flying Fish can be spread into wing-like shape. Certain species have pelvic fins shaped like wings which look like they have 2 pairs of wings. |
| * Flying Fish are shaped like a torpedo. Their fins are closed when they swim to ensure faster movement through the water. |
| * Before it emerges above the water, a Flying Fish accelerates toward the surface of the water with an average speed of 37 mph. When required speed is accomplished, a Flying Fish jumps out of the water and spreads its pectoral fins. |
| * Flying Fish can reach the height of 4 feet in the air and glide distance of 655 feet before returning back to the water. |
| * Flying Fish can travel a distance of 1,312 feet without rest. This is important because it ensures quick escape from predators. |
| * Main predators of Flying Fish are Marlin, Tuna, Swordfish, Mackerel and Humans. |
| * Flying Fish swim in large groups called schools. This feature is especially appreciated by fishermen that can catch large number of Flying Fish when they bump into a single school. |
| * Flying Fish are very sensitive and easily attracted by the light (fishermen use light to guide flying fish toward their ships). Despite that fact, Flying Fish hunt mainly during the night. |
| * Flying Fish eats plankton, bacteria and other tiny marine creatures. |
| * Mating season of Flying Fish takes place when the ocean currents are the weakest. Depending on the ocean, it can be during spring or autumn. |
| * Flying Fish live in large schools at previously mentioned and their number can exceed million individuals during the mating season. Females deposit large number of eggs near the surface of the water. |
| * Eggs are usually attached to the floating debris. Young Flying Fish have whiskers near the mouths and they look like the underwater plants. This appearance ensures survival during the first few days of life, when the youngsters are the most vulnerable. |
| * The average lifespan of Flying Fish is around 5 years. |