“Somniosus microcephalus”
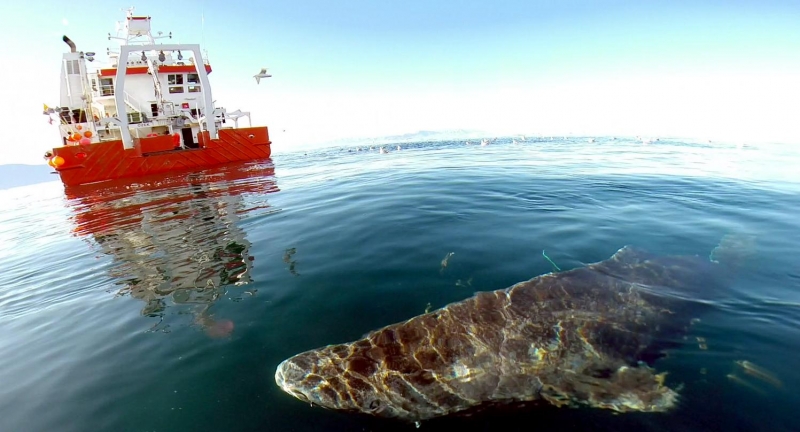
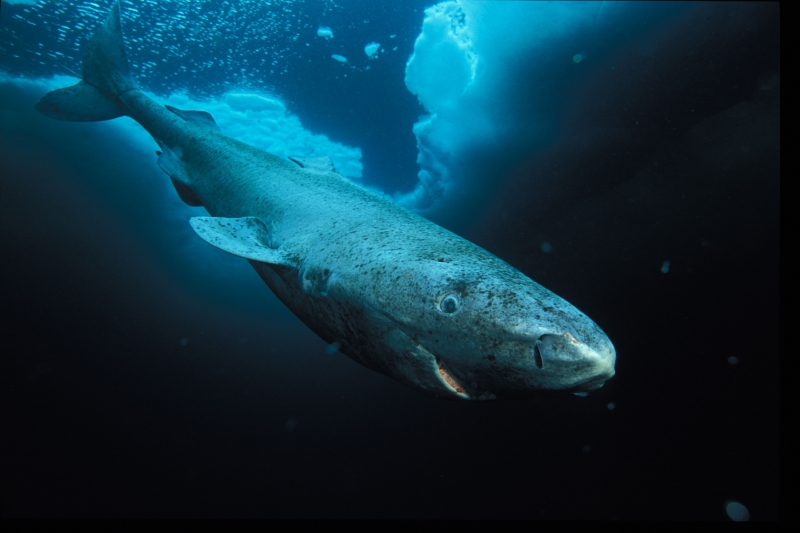
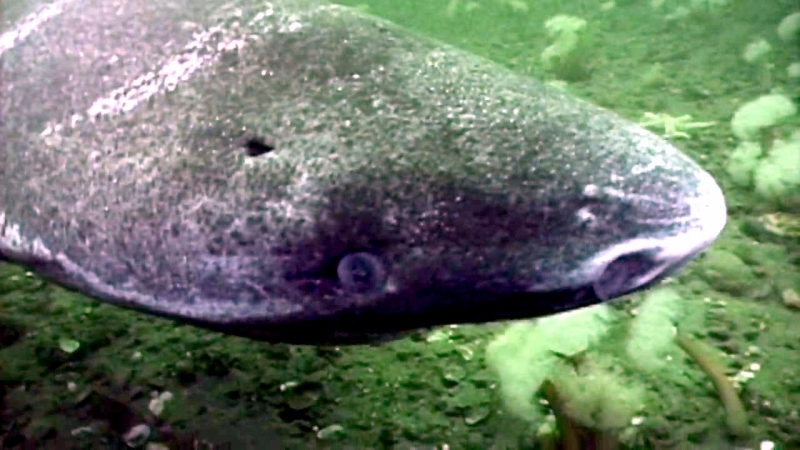
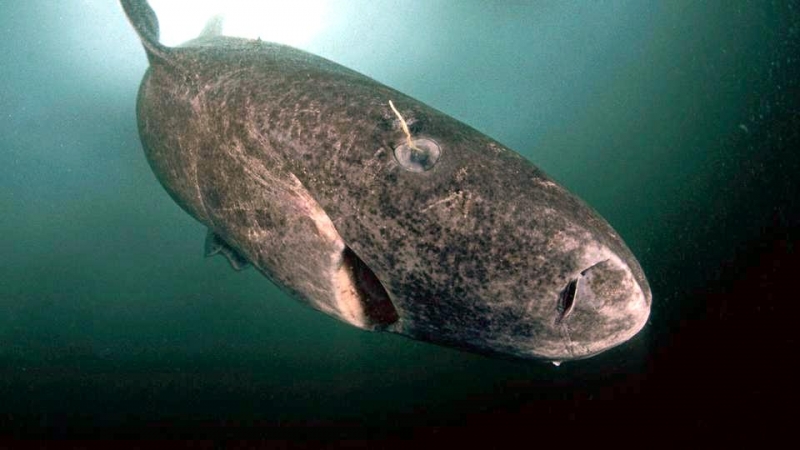
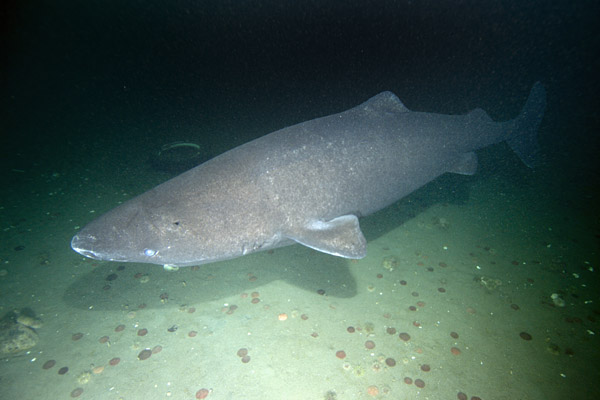
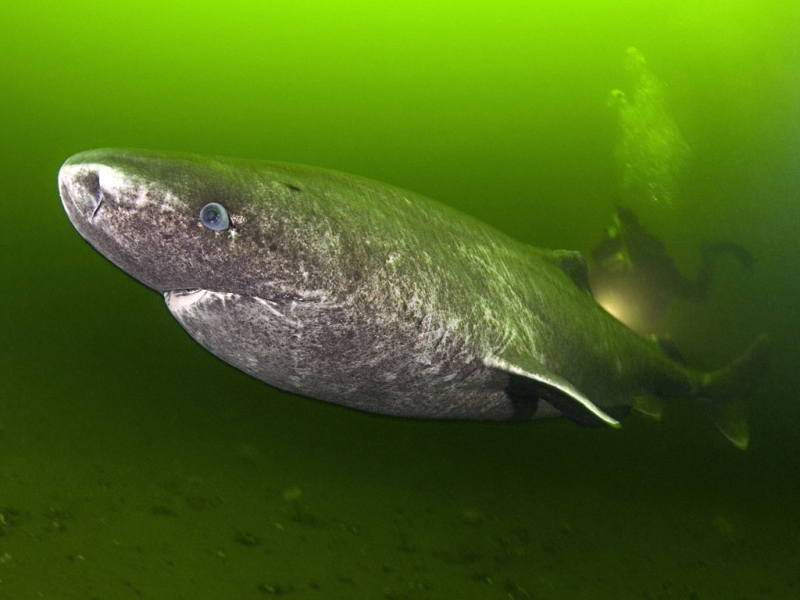
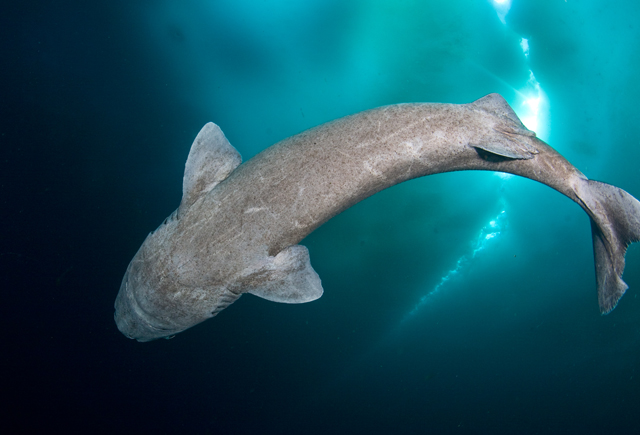
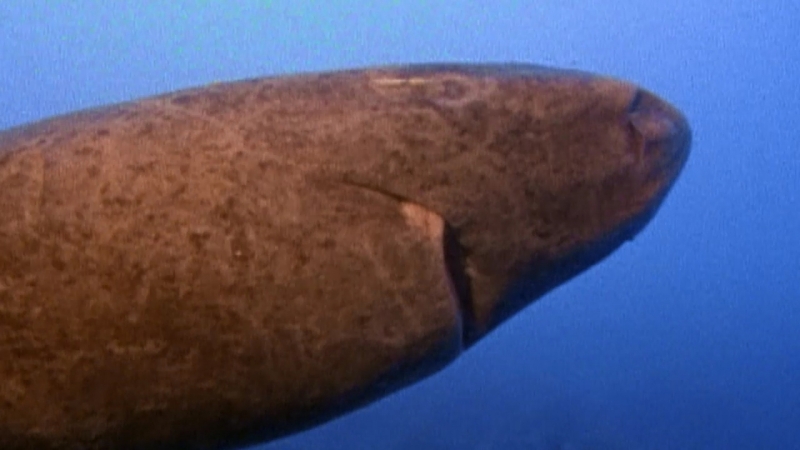
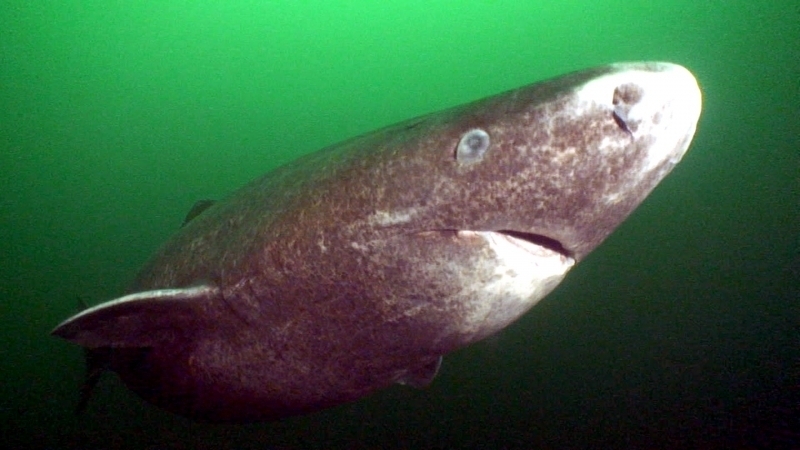
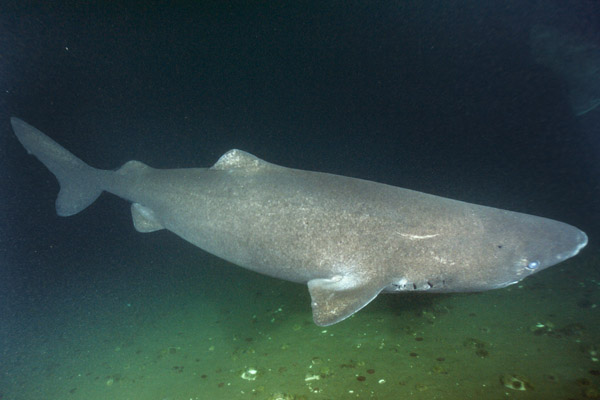
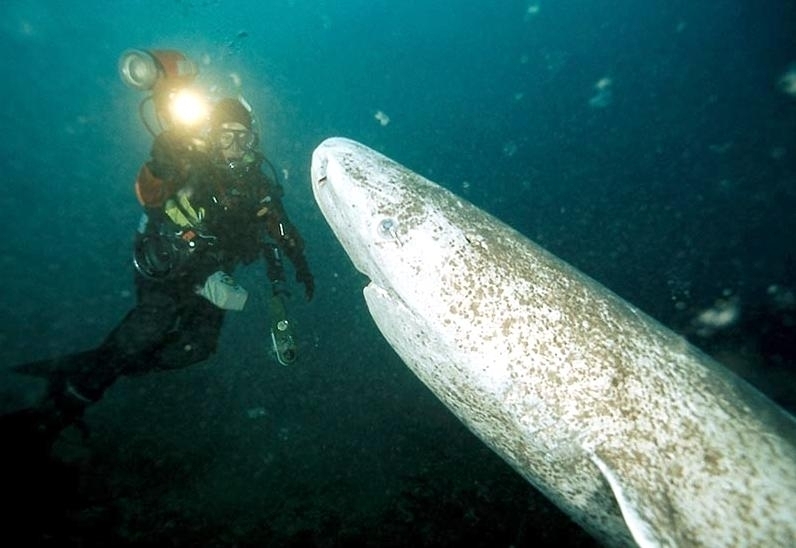
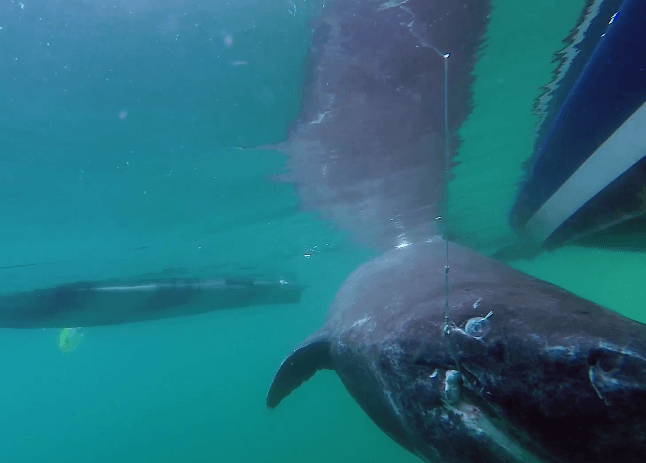
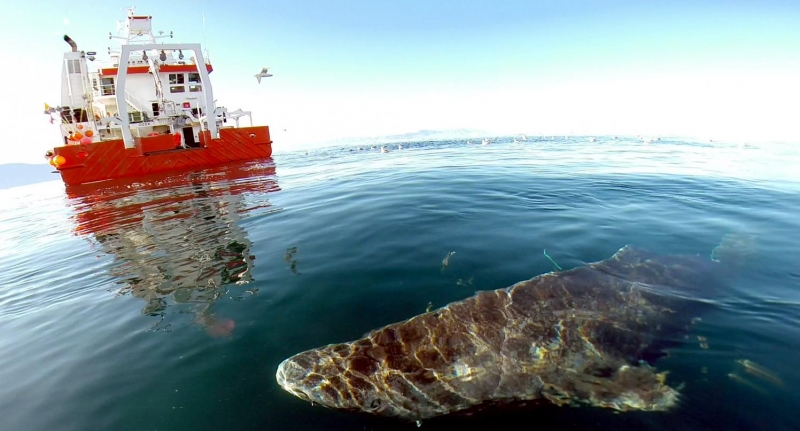
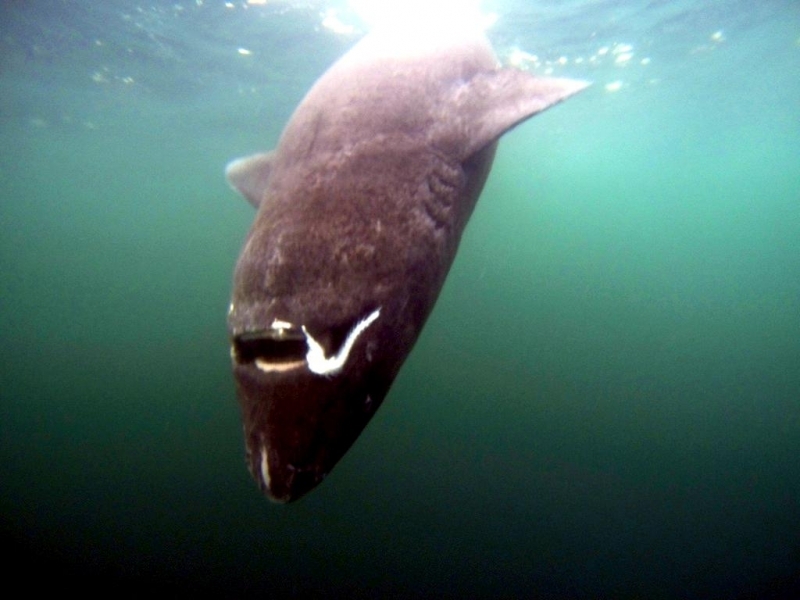
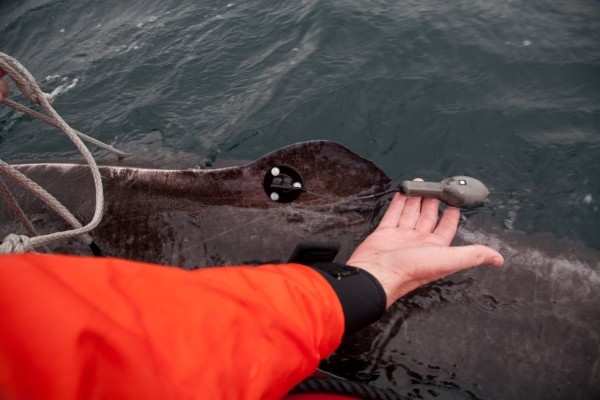
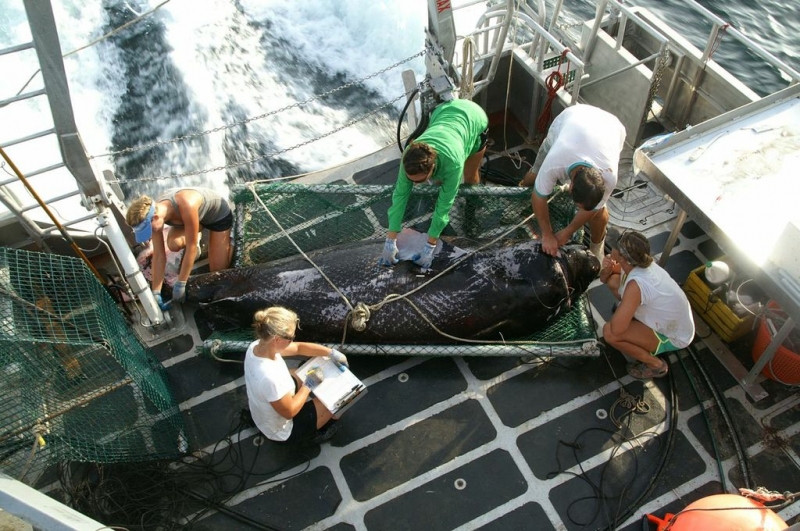
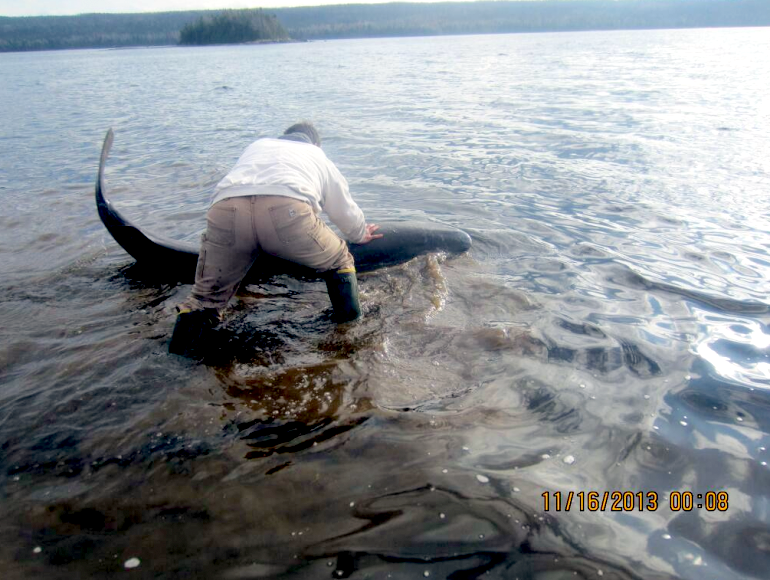
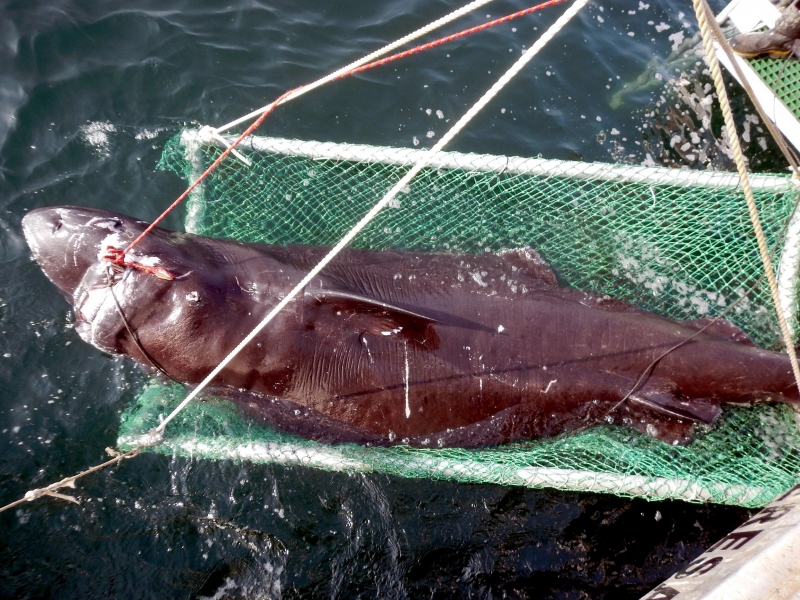
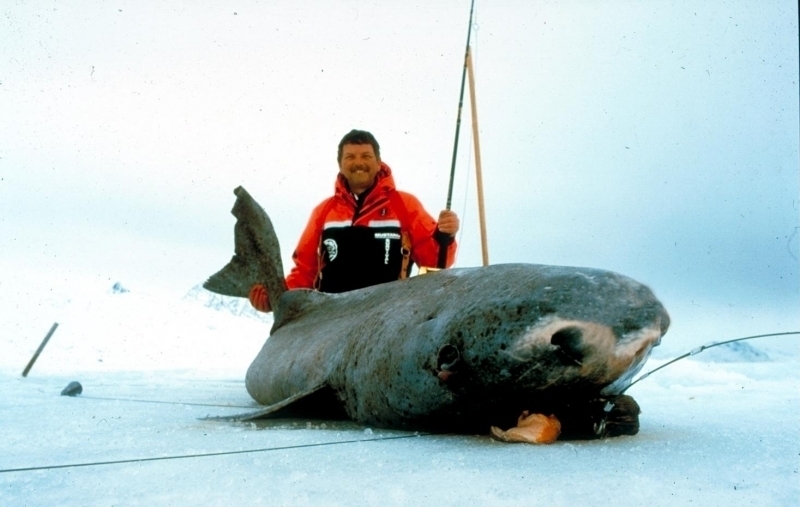
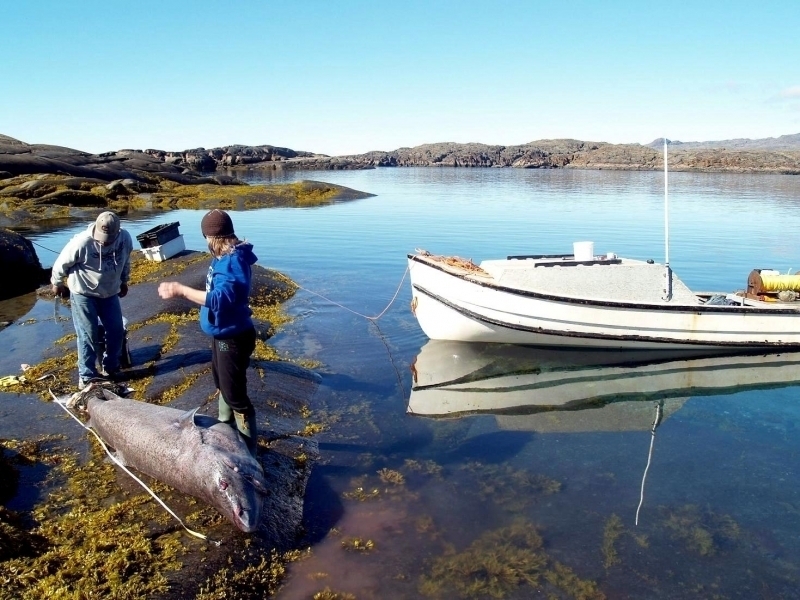
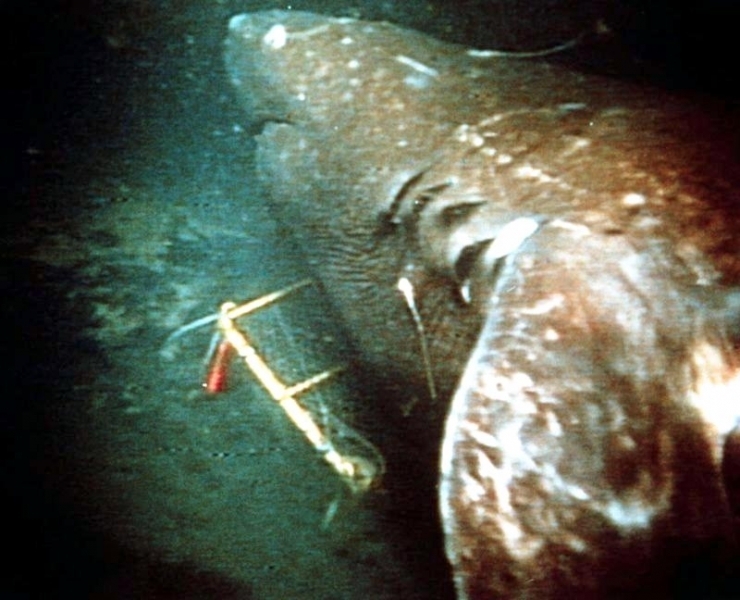
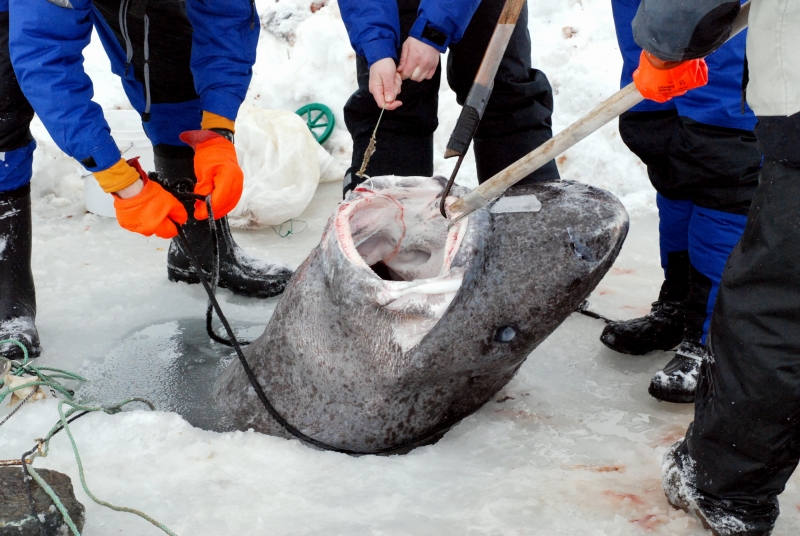
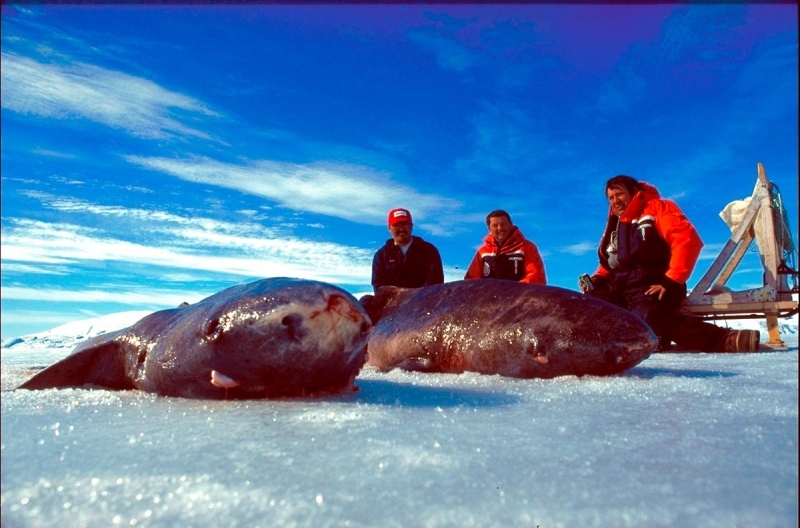
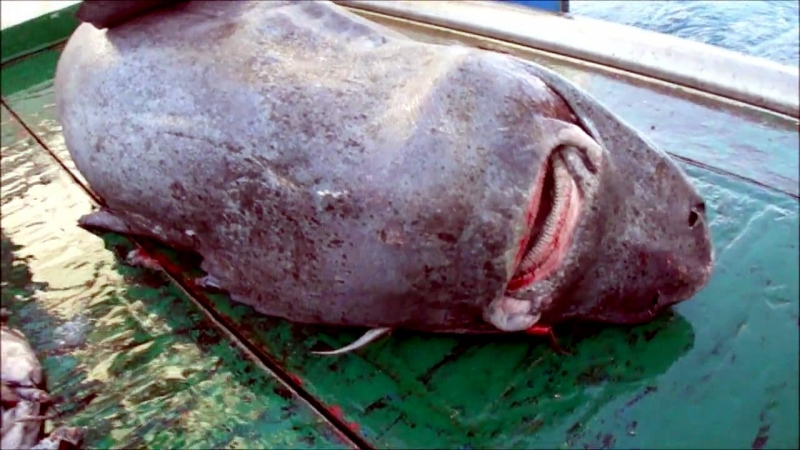
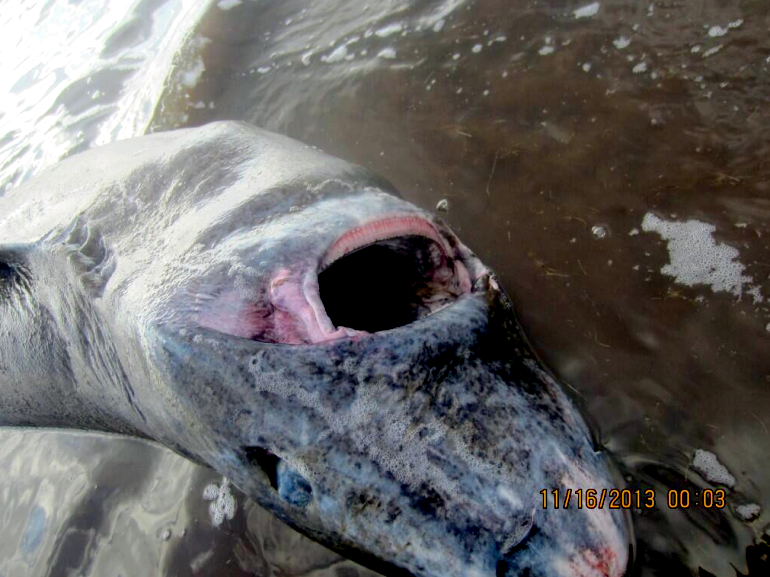
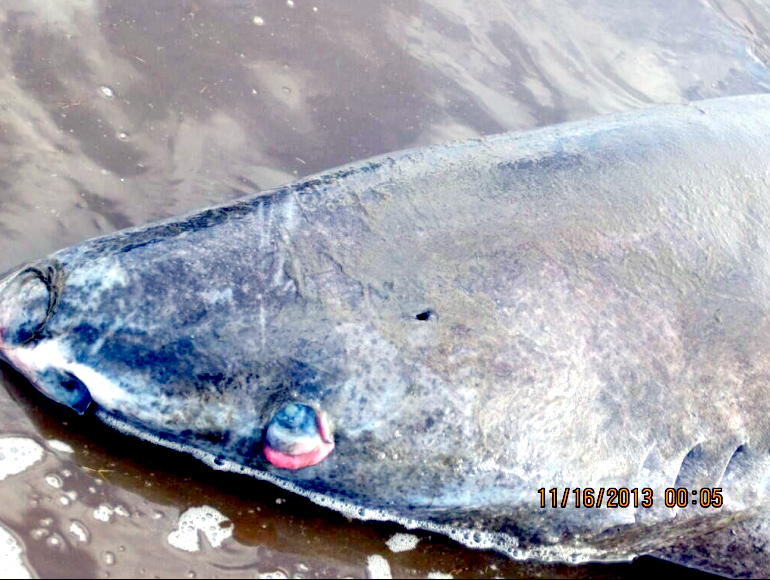
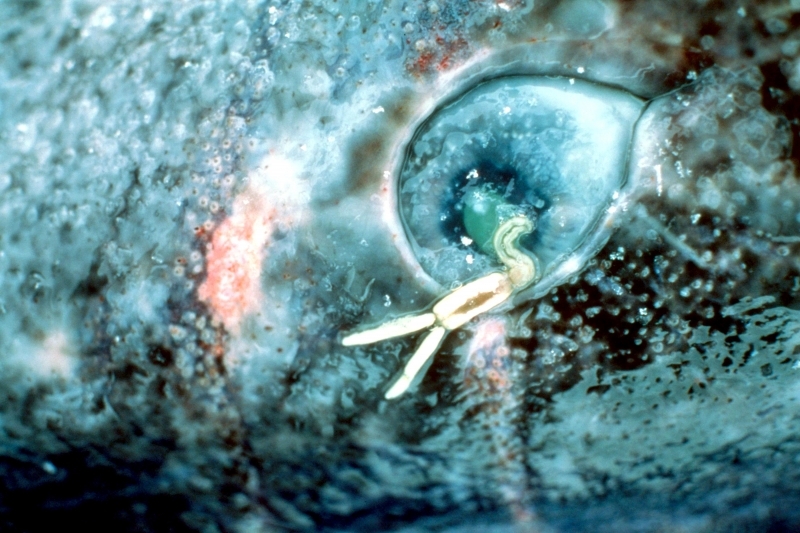
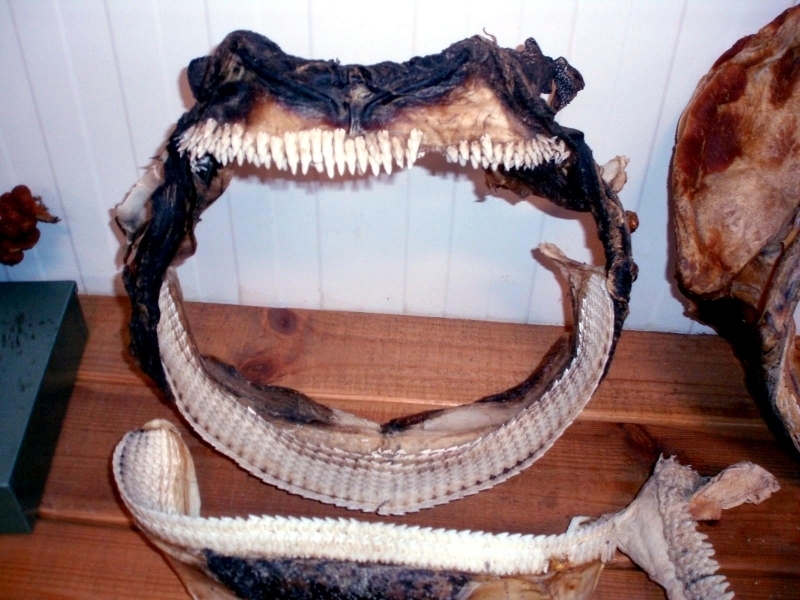
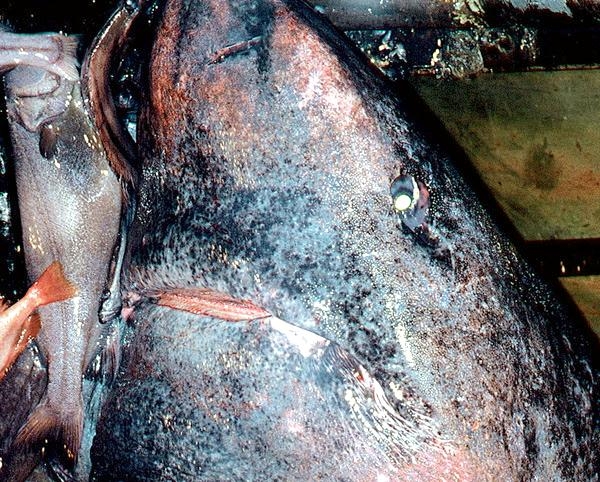
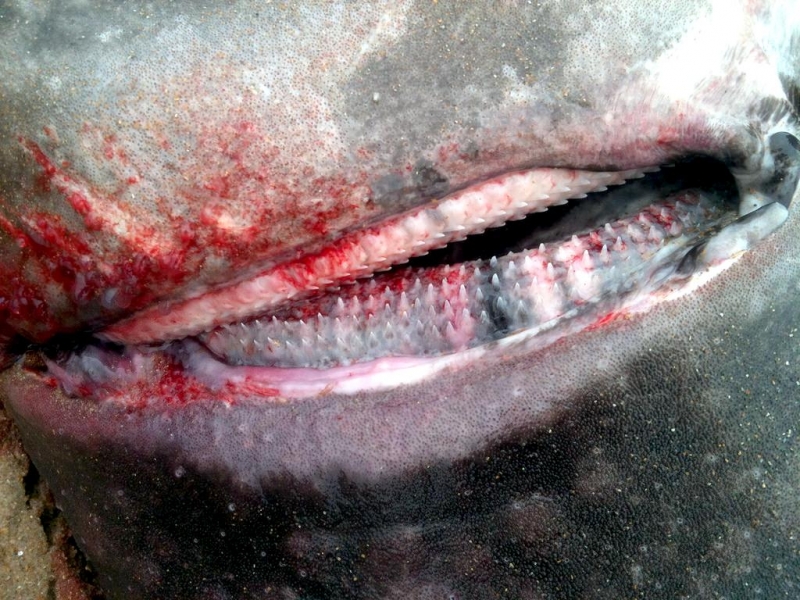
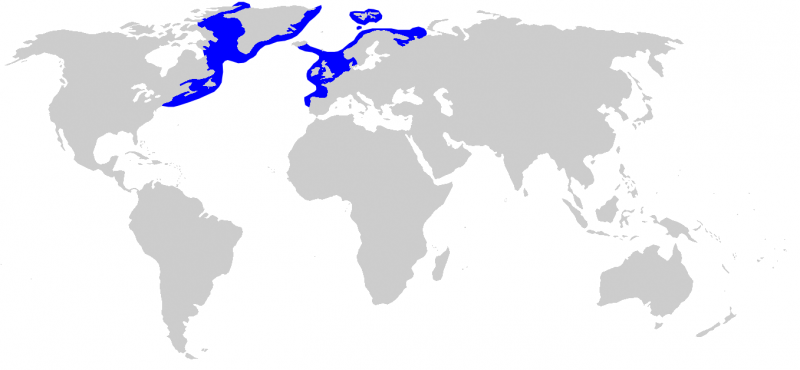
Greenland Sharks are named for their lethargic behavior; Somniosus which refers to “sleep” and microcephalus which means “small head”. In spite of their small heads, Greenland Sharks are large, robust sharks that reach up to 6.5 meters in length and weigh up to 900 kilograms. With an life expectancy of at least 272 years, the Greenland Shark has been recognized as the longest living vertebrate animal on the planet and how long they can live is still a mystery. They have short, rounded snouts, small eyes and small but sharp teeth. Their dorsal & pectoral fins are also quite small, as are their gill slits in relation to their body size. They are brown, gray or black in color and some may have dark lines or white spots on their dorsal (upper) sides or along their flanks. Greenland Sharks are found between 80°N-55°S in the northern Atlantic & Arctic regions, although sightings have been reported south near France & Portugal, as far west as the Gulf of St. Lawrence and as far south as off Cape Cod & North Carolina. Sightings have also been reported in the Southern Atlantic near Argentina and even in Antarctic waters.
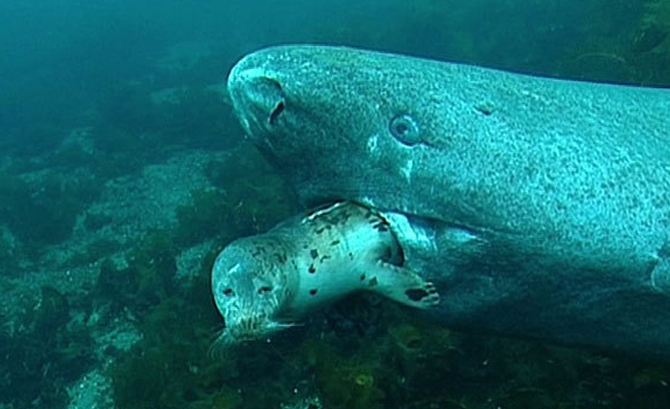
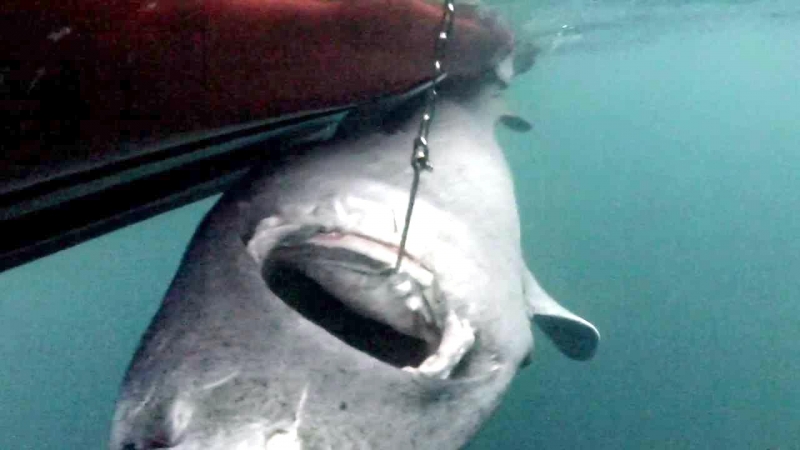
Greenland Sharks are a deep-water species that inhabits cold waters between 1-12 °C near the continental shelves & upper slopes down to at least 1,200 meters. In the Arctic & sub-arctic Atlantic however, Greenland Sharks can be found during the colder months inshore in inter-tidal areas and even at the surface of shallow bays & river mouths. Greenland Sharks feed on pelagic (open water), bottom fishes, other sharks, skates, eels, seals, small cetaceans, seabirds, squids, crabs, amphipods, marine snails, brittle stars, sea urchins & sea jellies. Greenland Sharks are also known to feed on carrion including reindeer and a recorded dead horse. Greenland Sharks are preyed upon by Sperm Whales, larger sharks and possibly Killer Whales. Greenland Sharks are an oviparous species. Pups measure about 38 centimeters at birth and litter size is between 5 to 10 young. The eggs are retained within the body of the female in a brood chamber where the embryo develops, receiving nourishment from a yolk sac. This is the method of reproduction for the “live-bearing” fishes where Greenland Shark pups hatch from egg capsules inside the mother’s uterus and are born soon afterward.