“Balaenoptera bonaerensis”
Dwarf Minke Whales were first described in the mid-1980’s even though there is still little known on them. This was after they attracted attention from scientists for frequently approaching waters in the northern Great Barrier Reef disrupting swimmers. It is on record that Dwarf Minke Whales are the second smallest type of baleen whales just after the Pygmy Right Whale. Upon maturation after 6-8 years, males measure about 23 feet while females measure an average of about 24 feet long. These lengths however can range from 29-32 feet in males and 31-35 feet in females. Both sexes on average weight between 4.4-5.5 tons although they can weigh up to 10 tons. A typical Dwarf Minke Whale bears a black/purple or grey in color. Their bodies are generally dark-grey or black with a white band underneath. They actually have between 240-360 baleen plates on each side. A Dwarf Minke Whale’s shoulder is whitish but with a flipper base having a dark-grey tip. Unlike Minke Whales, the Dwarf Minke Whale has a huge protruding patch making its way to the throat.
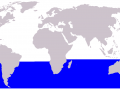
Dwarf Minke Whales have so far been described in the Southern Hemisphere only as well as Antarctic as opposed to the Northern Hemisphere. They are commonly found in Australian waters as well as waters of New Zealand, Vanuatu, South Africa, South Africa, Caledonia and east coast of South America. In Australian, they are present in almost all states except Tasmania but not at all in the Northern territory. Moreover, they frequent the Swains Reefs and the north of Lizard Island which are part of the Great Barrier Reef. The life span of Dwarf Minke Whales is so far unknown although other Minke Whales live between 50-60 years. Their life spans are projected by physically finding the estimate number of waxy plug layers around the ear drum. New layers are ideally deposited every year. They reach sexual maturity after 6-8 years when they are 6.5 meters long. Based on facts known about other Minke Whales, Dwarf Minke Whales probably give birth to one 2 meters long calf each year and suckle them during those early ages with milk containing about 30% fat. Calves are usually weaned between 5-6 months after birth. The Dwarf Minke Whales are not easily distinguishable. Other huge whales like the Humpback Whale, migrate to the higher latitudes to feed and move back to the lower latitudes to calve and nurse. However, little is known as regards the feeding patterns of Dwarf Minke Whales.